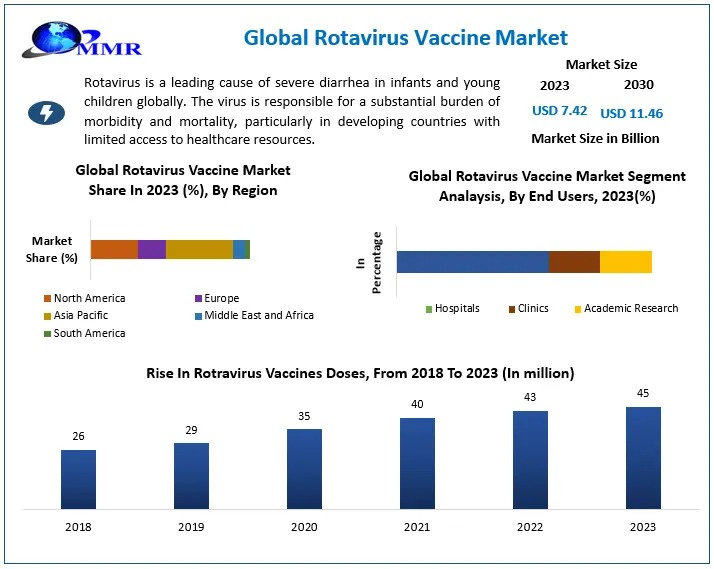
The future of healthcare Care Agency in Manchester is no longer a distant dream—it’s unfolding right before our eyes. Technological advancements, personalized medicine, and a more patient-centered approach are transforming the way we deliver, receive, and think about healthcare. From the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics to telemedicine and wearable technology, the healthcare industry is on the verge of a revolution that promises to improve outcomes, reduce costs, and make care more accessible.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn this blog, we’ll explore how the future of healthcare is becoming a reality and the key innovations driving these changes.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are reshaping healthcare, particularly in diagnostics and predictive analytics. AI-driven tools can analyze vast amounts of medical data, helping doctors detect diseases more accurately and earlier than ever before. AI is already being used to analyze medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect abnormalities like tumors or fractures that may not be easily visible to the human eye.
AI can also predict patient outcomes by analyzing medical histories and risk factors. For example, IBM’s Watson Health has been used to predict cancer risks and recommend treatment options based on the patient’s genetic makeup and medical history. As AI and ML technologies continue to advance, they will improve diagnosis accuracy, reduce human error, and lead to more personalized care.
Real-World Example:
AI is currently being used in breast cancer screenings to assist radiologists. A study published in The Lancet in 2020 showed that AI systems could reduce false positives and false negatives, helping in early detection and treatment of breast cancer.
Telemedicine and Virtual Care
Telemedicine has seen rapid growth in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced healthcare systems to rethink how care is delivered. Through virtual consultations, patients can now receive medical advice, diagnoses, and even prescriptions from the comfort of their homes. Telemedicine has bridged the gap for those who live in remote areas or have limited access to healthcare facilities, making care more accessible and efficient.
Beyond video consultations, virtual care includes remote monitoring of patients using wearable devices that track vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. Doctors can monitor patients in real-time and make adjustments to treatments as necessary without the patient needing to visit a clinic or hospital.
Real-World Example:
Companies like Teladoc Health and Amwell have provided millions of virtual consultations, allowing patients to receive healthcare services even during the height of the pandemic. This technology is especially useful for managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, where continuous monitoring is essential.
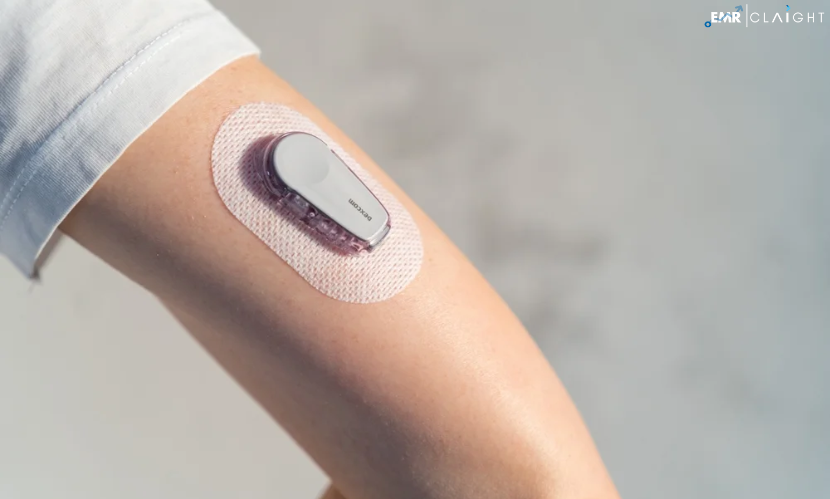
Wearable Health Technology
Wearable devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical wearables are empowering individuals to take charge of their health. These devices can monitor physical activity, sleep patterns, heart rate, and other vital signs, providing users with real-time insights into their health. In the future, wearable technology will become more advanced, offering real-time alerts for potential health issues like irregular heartbeats or elevated blood pressure.
Beyond fitness tracking, wearable medical devices can monitor conditions like diabetes, with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) becoming more prevalent. The data collected from these devices can be shared with healthcare providers, enabling them to make more informed decisions and provide personalized care.
Real-World Example:
The Apple Watch Series 6 includes a blood oxygen sensor and an ECG app, allowing users to monitor their cardiovascular health and detect issues such as atrial fibrillation (AFib). These advancements in wearable technology help users stay proactive about their health and seek medical intervention when necessary.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized or precision medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This approach moves away from the “one-size-fits-all” treatment model and instead focuses on developing treatments that work best for a particular individual.
Advancements in genetic sequencing and biotechnology have made it possible to develop personalized treatments, particularly in fields like oncology. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, doctors can determine the most effective treatments for conditions like cancer, ensuring that patients receive therapies tailored to their unique biology.
Real-World Example:
Pharmacogenomics, which studies how a person’s genes affect their response to drugs, is being used to develop more effective cancer treatments. For instance, certain lung cancer patients with specific genetic mutations may benefit from targeted therapies, such as the drug crizotinib, which is designed to treat tumors driven by ALK gene mutations.
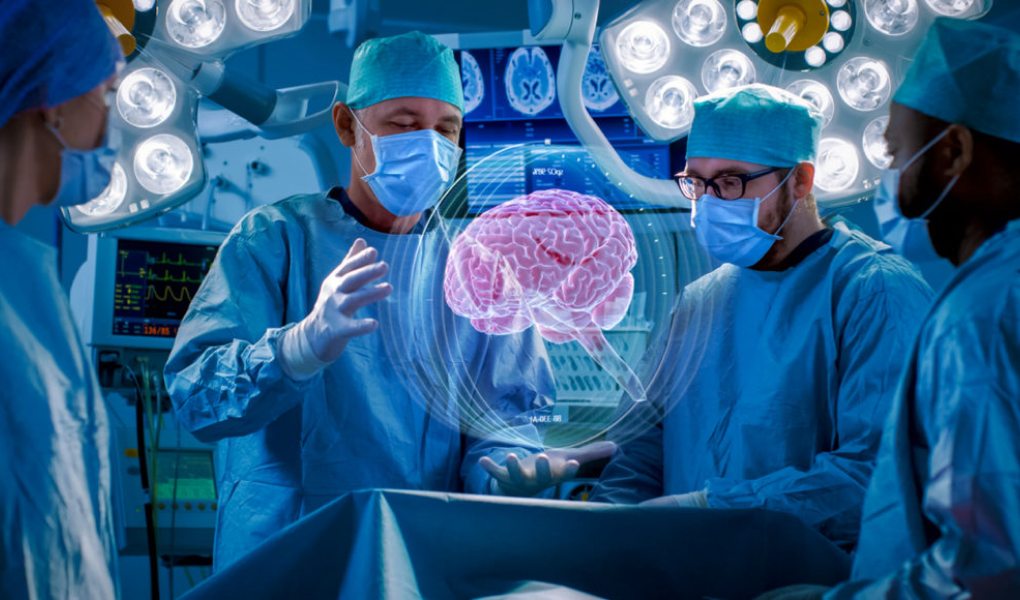
Robotics and Minimally Invasive Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery has been a game-changer in the world of healthcare. These advanced surgical systems, like the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with greater precision and control. Robots assist with complex surgeries that require extreme delicacy, such as heart or neurosurgery, reducing the risks of complications, improving recovery times, and minimizing scars.
As robotic technology continues to advance, we may see more autonomous surgical robots capable of performing routine surgeries with minimal human intervention. This would drastically reduce the costs and risks associated with surgeries, making them safer and more accessible to patients worldwide.
Real-World Example:
The da Vinci Surgical System is already being used in hospitals around the world for minimally invasive procedures, such as prostatectomies and hysterectomies. The system provides surgeons with a 3D view of the surgical area and allows them to make more precise movements through small incisions.
Genomics and Gene Editing
Genomics, the study of an individual’s entire genetic code, is playing an increasingly important role in the future of healthcare. By analyzing DNA, scientists can identify genetic predispositions to diseases, helping in the early diagnosis and prevention of conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
Gene-editing technologies like CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) are also opening up new possibilities for treating genetic disorders. CRISPR allows scientists to edit genes to correct mutations, potentially curing genetic diseases at their source.
Real-World Example:
CRISPR technology has been used in clinical trials to treat genetic disorders such as sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia. Early results have shown that gene editing could offer long-term cures for these previously untreatable conditions.
Big Data and Predictive Analytics
Big data is transforming healthcare by providing insights that were previously unimaginable. With the vast amount of medical data now available—from electronic health records (EHRs) to data collected from wearable devices—healthcare providers can analyze patterns, predict health trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve patient outcomes.
Predictive analytics, powered by AI and big data, can help forecast disease outbreaks, manage patient populations, and personalize treatment plans. This shift toward data-driven healthcare will allow for more proactive care, where doctors can intervene before a condition worsens, rather than reacting after the fact.
Real-World Example:
Health systems like Kaiser Permanente are using predictive analytics to identify patients at risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. By analyzing patient data, they can intervene early with preventive care, reducing hospitalizations and improving long-term health outcomes.
3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing is being used in healthcare to create everything from prosthetics to organ models. Customized prosthetic limbs can now be 3D printed to fit each patient’s unique anatomy, improving comfort and function. Surgeons can use 3D-printed models of organs to plan complex surgeries, increasing precision and reducing risks.
In the future, bioprinting—using 3D printers to create human tissues and organs—could revolutionize organ transplants by making it possible to “print” organs from a patient’s own cells, eliminating the need for donors and reducing the risk of rejection.
Real-World Example:
Doctors at the Mayo Clinic have used 3D printing to create custom prosthetic implants for patients with complex bone deformities. 3D-printed organ models have also been used to help surgeons plan delicate operations, such as separating conjoined twins.
Conclusion
The future of healthcare is becoming a reality as technological innovations continue to improve diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. From AI and robotics to personalized medicine and wearable technology, these advancements are reshaping the way healthcare is delivered, making it more accessible, efficient, and tailored to individual needs.
As these technologies continue to evolve, the possibilities for improving health outcomes are limitless. We are entering an era where healthcare will become more predictive, preventative, and personalized, offering better solutions for patients and revolutionizing the way we think about medicine. The future of healthcare is here and it’s changing lives for the better.